
Harmonizing Health: How ICH Guidelines Regulate Pharma
Medicine production is based on three pillars: quality, safety, and efficacy. Everyone involved in pharmaceutics – from researchers and pharmaceutical companies to regulatory organizations – is responsible for maintaining these pillars. In this regard, the International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, more commonly known as ICH, plays a pivotal role. In this article, we provide insights in ICH’s significance, structure, and guidelines.
Origin and Rise to Prominence
Established in 1990, ICH aims to harmonize the regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical products around the globe. Initially constituted by members from Europe, Japan, and the US, ICH has since expanded to include more members worldwide. The primary goal of the council is to ensure the development, registration, and efficient production of safe, effective, and high-quality medicines. ICH aims to reduce duplicate testing during the research phases of new products, saving both time and resources.
ICH Structure
ICH is structured in a well-defined way (see Figure 1). The Assembly serves as the overarching governing body of ICH, responsible for adopting new ICH guidelines and steering the organization’s overall activities. Finance and administration fall under the responsibilities of the ICH Management Committee, ensuring the efficient functioning of the organization. The MedDRA Management Committee oversees the maintenance and development of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA), which contains international and standardized medical terminology intended to ease the exchange of regulatory information. Lastly, there are several ICH Working Groups that are responsible for developing new ICH guidelines. Working groups consist of experts coming from industry as well as regulatory authorities. Together, they draft, review, and finalize the ICH guidelines.
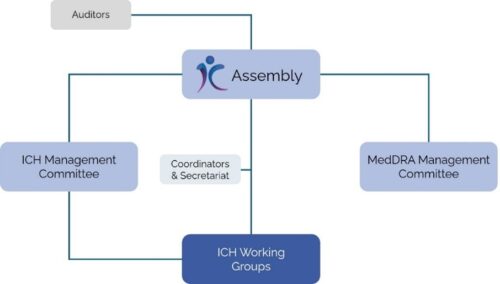
Figure 1. ICH structure (modified from: https://www.ich.org/PAGE/ORGANISATION-ICH)
ICH Guidelines
The ICH guidelines are categorized into four main areas: Quality, Safety, Efficacy, and Multidisciplinary guidelines. They each address certain aspects of pharmaceutical development and regulation.
Quality Guidelines
Quality guidelines ensure that pharmaceutical products meet high standards of quality throughout their lifecycle.
These guidelines include, for example:
stability testing of new drugs and products (Q1A), good manufacturing practice guide for active pharmaceutical ingredients (Q7), and quality risk management (Q9).
Safety Guidelines
Safety guidelines are designed to ensure that pharmaceutical products are safe for human use. They handle a wide variety of nonclinical and clinical safety topics, ranging from carcinogenicity (S1) over immunotoxicology (S8) to gene therapy (S12).
Efficacy Guidelines
Efficacy guidelines focus on everything involved in the development of clinical trials and are crucial for demonstrating the therapeutic benefits of pharmaceutical products. While all efficacy guidelines are highly important for the conduct of clinical trials, efficacy guidelines that are particularly useful for medical writers include ICH E3, E6, E8, and E9.
The ICH E3 guideline focuses on the structure and content of clinical study reports to be submitted to the regulatory authorities.
The ICH E6 guideline is better known as the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guideline. It provides a comprehensive and standardized overview of how to design, conduct, and report clinical trials. This guideline is crucial for ensuring patient safety and protecting data security. Particularly useful for medical writers is its guidance for drafting a clinical trial protocol and an investigator’s brochure, as well as the overview of essential documents for the conduct of a clinical trial.
The ICH E8 and E9 guidelines include general considerations for the design and conduct of clinical trials and for statistical principles to take into account when aiming for marketing authorization, respectively.
Multidisciplinary Guidelines
Lastly, there are the multidisciplinary guidelines, covering any remaining topics, such as gene therapy (M6) and use of real-world data in pharmacoepidemiological studies (M14).
Particularly useful for medical writers, is the guidance on the Common Technical Document (CTD) (M4, M4Q, M4S, and M4E). The CTD assembles all information related to the quality, safety, and efficacy of a pharmaceutical product under development, including
- regional administrative information and prescribing information,
- the quality overall summary, nonclinical overview, clinical overview, nonclinical written and tabulated summaries, and clinical summary,
- structured information on quality,
- nonclinical study reports,
- and clinical study reports.
The CTD is mandatory (in the EU & Japan) or at least strongly recommended (in the US) for new drug applications, allows harmonization, central electronic submission, and standardized review processes by the regulatory authorities.
Development of ICH Guidelines
All ICH guidelines can be browsed using the Index of Guidelines on the ICH website, including the guidelines that are still under development.
Development of new ICH guidelines occurs through a transparent standardized operating procedure:
- New topic proposed by an ICH Member or Observer for endorsement by the ICH Assembly
- Informal Working Group established that develops a Concept Paper to provide further context and define the objectives
- Expert Working Group or Implementation Working Group established that develops a detailed Work Plan to constitute milestones and deadlines
o Step 1: Prepare an initial consensus draft
o Step 2: Endorsement of the consensus text by the ICH Assembly and adoption of the Draft Guideline by Regulatory Members
o Step 3: Regional regulatory consultation, discussion of regional comments, and sign-off by regulatory experts
o Step 4: Adoption of the ICH Harmonized Guideline
o Step 5: Implementation by each of the Regulatory Members
Accordingly, different standardized operating procedures exist for the development of Q&A documents and the revision or correction of existing ICH guidelines.
Conclusion
This article highlights the impact of ICH on the healthcare industry. By providing a clear framework and fostering collaboration between regulatory and industry experts, ICH ensures the development of high-quality medicines.
Emtex Life Science medical writers are continuously kept up-to-date with recent advancements and key updates in the ICH guidelines. This is fundamental for meeting the high quality standards in regulatory medical writing.